Determining the Medical Device Classification and related classification rule is the first step in the EU CE Marking process. Technical file and Notified Body application can be made according to the class and rule of the device.
According to Article 51 of EU MDR 2017/745, medical devices are classified as I, IIa, IIb and III, taking into account their intended use and the risks involved. The risk increases from class I to class III. The EU Medical Device Directive (MDD) and the EU Medical Device Directive (MDR) use a rule-based classification model for medical devices. The new MDR now has 22 rules in Annex VIII.
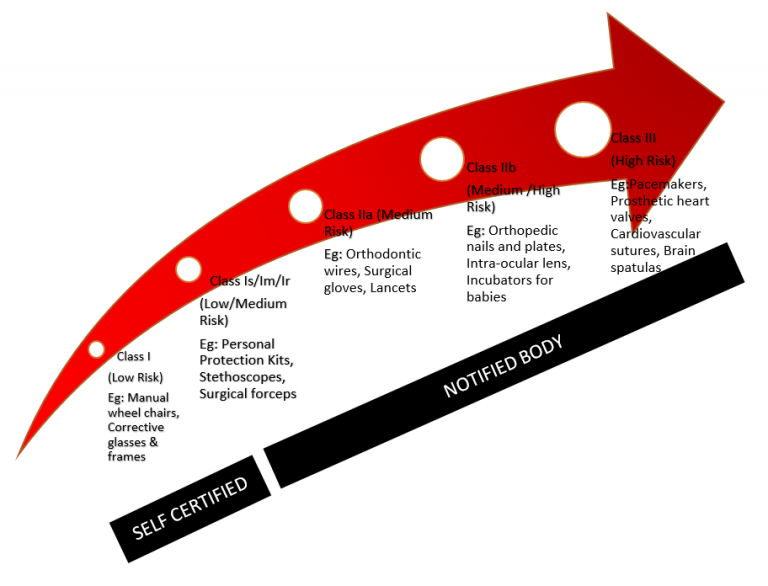
Class I – Low Risk
Examples: Corrective glasses and frames, Manual wheelchairs
Certification Type: Self-Certification / Declaration
Class 1s – Low Risk (Sterile)
Examples: Personal protection kits, Sterile Urine Bags etc.
Certification Type: Notified Body
Class 1m Low Risk (Measuring Body Properties)
Examples: Stethoscopes, Weighing Scales
Certification Type: Notified Body
Class 1r Low Risk (Reused Device)
Examples: Surgical forceps (All types of SS/Tit surgical equipment are sterilized and reused by hospitals)
Certification Type: Notified Body
Class IIa – Moderate Risk
Examples: Orthodontic wires, Surgical gloves, Lancets
Certification Type: Notified Body
Class IIb – Moderate and High Risk
Examples: Orthopedic nails and plates, Intraocular lens, Incubators for babies
Certification Type: Notified Body
Class III – High Risk
Examples: Pacemakers, Prosthetic heart valves, Cardiovascular sutures, Brain spatulas, Drug-Device Combination products
Certification Type: Notified Body
Medical Device Classification Rules
In accordance with MDR Annex VIII, the Classification Rules are as follows:
- Rule 1- 4: Non-invasive Devices
- Rule 5 – 8: Invasive Devices
- Rule 9 – 13: Active Devices
- Rule 14 – 22: Special Rules
IVDR Classification
IVDR Classification is based on the intended use and inherent risks of In-Vitro Diagnostic Devices (IVDs), therefore they are classified into classes A, B, C and D, taking into account their intended use and inherent risks.
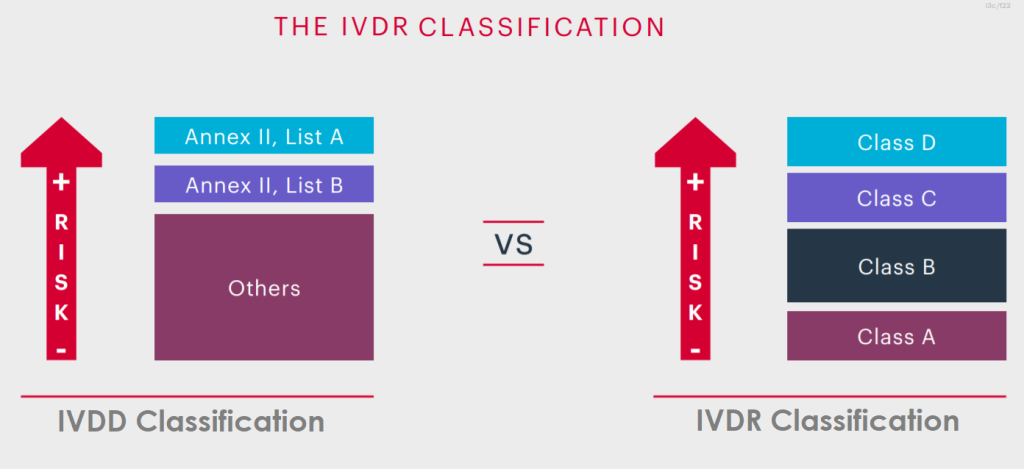
How are In-Vitro Diagnostic Devices classified in IVDR?
In-Vitro Diagnostic Devices or IVDs are classified in classes A, B, C and D, taking into account their intended purpose and inherent risks. It is classified from the lowest risk category in Class A to the highest risk category in Class D.
Class D (High personal risk, High public health risk)
Examples: Blood grouping ABO, Rhesus (including RHW1), Kell, Kidd and Duffy systems, CHAGAS, Syphilis (used for screening blood donations), Hepatitis B and C etc.
According to the IVDR Classification for Class D IVDs, CE marking can be obtained by conformity assessment methods:
Quality Management System Assurance [Annex IX], then Technical Documentation Evaluation [Annex IX Part II] followed by Verification by the EU Reference Laboratory
OR
Type Examination [Annex X] (includes Technical Documents), followed by Production Quality Assurance [Annex XI], followed by Verification by the EU Reference Laboratory
Class C (High personal risk, Moderate to low public health risk)
Examples: Genetic tests, Ancillary diagnostics, Blood gas analyzers, Cancer markers, Rubella, Newborn screening for metabolic disorders etc.
According to the IVDR Classification for Class C IVDs, CE marking can be obtained through conformity assessment methods:
Quality Management System Assurance [Annex IX], followed by Evaluation of Technical Documentation per generic device [Annex IX 4.4-4.8] followed by Competent Authority consultation for Associate Diagnosis [Annex IX 5.2]
OR
Type Examination [Annex X] (includes Technical Documentation), followed by Production Quality Assurance [Annex XI] followed by Competent Authority consultation for Assistant Diagnosis [Annex X 3]
Class B (Moderate to low personal risk, Low public health risk)
Examples: Thyroid function tests, Infertility tests, Clinical Chemistry
According to IVDR Classification for Class B IVDs, CE marking can be obtained through conformity assessment.
Quality Management System Assurance [Annex IX] followed by Evaluation of Technical Documentation per category device [Annex IX 4.4-4.8].
Class A (Low personal risk, Low public health risk)
Instruments, Sample cups, Wash pads etc.
For Class A IVDs, CE marking can be obtained through conformity assessment.
EU Declaration of Conformity [Annex III].